|
受注:045-509-1970 |
技術サポート:[email protected] 平日9:00〜18:00 1営業日以内にご連絡を差し上げます |
化学情報
|
Synonyms | ASA404, NSC 640488 | Storage (From the date of receipt) |
3 years -20°C powder 1 years -80°C in solvent |
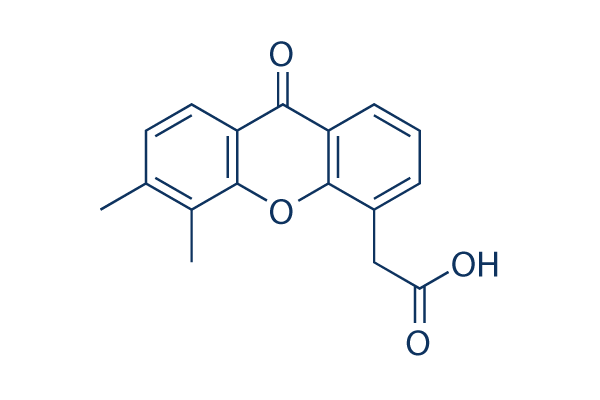
| 化学式 | C17H14O4 |
|||
| 分子量 | 282.29 | CAS No. | 117570-53-3 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | 体外 | DMSO | 6 mg/mL (21.25 mM) | |
| Water | Insoluble | |||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. |
||||
溶剤液(一定の濃度)を調合する
生物活性
| 製品説明 | Vadimezan (DMXAA) is a vascular disrupting agents (VDA) and competitive inhibitor of DT-diaphorase with Ki of 20 μM and IC50 of 62.5 μM in cell-free assays, respectively. DMXAA (Vadimezan) is also a STING agonist with potential antineoplastic activity. DMXAA (Vadimezan) potently induces IFN-β but relatively low TNF-α expression in vitro. DMXAA (Vadimezan) has antiviral activity. Phase 3. |
|---|---|
| in vitro | In DLD-1 human colon carcinoma cells, DMXAA inhibits DT-diaphorase activity without significant effects on the activity of cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome P450 reductase. Combination of menadione and DMXAA leads to an increase in the antiproliferative activity of DLD-1 cells. [1] DMXAA, as an antiviral agent, inhibits VSV-induced cytotoxicity and influenza virus replication in RAW 264.7 macrophages. [2] A recent study shows that DMXAA has non-immune-mediated inhibitory effects against several kinase members of VEGFR (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor), such as VEGFR2 signalling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. [3] |
| in vivo | DMXAA treatment significantly protects C57BL/6J mice infected i.n. with 200 p.f.u. mouse-adapted H1N1 influenza PR8 virus with 60% survival, while the control group only exhibited 20% survival. [2] DMXAA significantly delays tumor growth induced by chemical carcinogen, increases the time to tumor doubling and increases time from treatment to euthanasia. After the treatment of DMXAA, median tumor doubling time, median tumour tripling time and median time from treatment to euthanasia in tumor-bearing animals are increased by approximately 4.4-, 1.8- and 2.7-fold, respectively. [4] |
プロトコル(参考用のみ)
| キナーゼアッセイ | DT-diaphorase activity and kinetic analysis of enzyme inhibition | |
|---|---|---|
| Purified DT-diaphorase enzyme activity is assayed by measuring the reduction of cytochrome c at 550 nm on a Beckman DU 650 spectrophotometer. Each assay contains cytochrome c (70 μM), NADH (variable concentrations), purified DT-diaphorase (0.032 μg), and menadione (variable concentrations) in a final volume of 1 mL Tris–HCl buffer (50 mM, pH 7.4) containing 0.14% BSA. The reaction is started by the addition of NADH. Rates of reduction are calculated over the initial part of the reaction curve (30 seconds), and results are expressed in terms of μmol cytochrome c reduced/min/mg protein using a molar extinction coefficient of 21.1 mM−1 cm−1 for reduced cytochrome c. Enzyme assays are carried out at room temperature and all reactions are performed in triplicate. Inhibition of purified DT-diaphorase activity is performed by the inclusion of DMXAA (at various concentrations) in the reaction, and inhibition characteristics are determined by varying the concentration of NADH (constant menadione) or menadione (constant NADH) at several concentrations of inhibitor. Ki values are obtained by plotting 1/V against. The activity of DT-diaphorase in DLD-1 cells is determined by measuring the dicumarol-sensitive reduction of DCPIP at 600 nm. Briefly, DLD-1 cells in mid-exponential growth are harvested by scraping into ice-cold buffer (Tris–HCl, 25 mM, pH 7.4 and 250 mM sucrose) and sonicated on ice. Enzyme assay conditions are 2 mM NADH, 40 μM DCPIP, 20 μL of dicumarol (when required) in a final volume of 1 mL Tris–HCl (25 mM, pH 7.4) containing BSA (0.7 mg/mL). Results are expressed as the dicumarol-sensitive reduction of DCPIP using a molar extinction coefficient of 21 mM−1 cm−1. Protein levels are determined using the Bradford assay | ||
| 細胞アッセイ | 細胞株 | DLD-1 and H460 cells |
| 濃度 | 0-2 mM | |
| 反応時間 | 96 hours | |
| 実験の流れ | DLD-1 human colon carcinoma and H460 human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells are routinely maintained as monolayer cultures in RPMI 1640 culture medium supplemented with foetal calf serum (10%), sodium pyruvate (2 mM), penicillin/streptomycin (50 IU mL−1/50 μg mL-1) and l-glutamine (2 mM). Chemosensitivity is assessed using the MTT assay and all assays are performed under aerobic conditions. Briefly, cells are plated into each well of a 96-well culture plate and incubated overnight in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. Culture medium is completely removed from each well and replaced with medium containing a range of drug concentrations. In the case of menadione alone, the duration of drug exposure is 1 hour, after which the cells are washed twice with Hanks' balanced salt solution prior to the addition of 200 μL fresh RPMI 1640 medium to each well of the plate. In the case of DMXAA alone, the duration of drug exposure is 3 hours. Following a four-day incubation, cell survival is determined using the MTT assay. For combinations of DMXAA with menadione, cells are initially set up and a non-toxic (>95% cell survival) concentration of DMXAA is selected. Cells are then initially exposed to DMXAA (2 mM) for a period of 2 hours, following which the medium is removed and replaced with medium containing the inhibitor (DMXAA at a constant concentration of 2 mM) and menadione (at a range of drug concentrations). Following a further 7-hour incubation, cells are washed twice with Hanks' balanced salt solution prior to the addition of growth medium. | |
| 動物実験 | 動物モデル | Chemical carcinogen (NMU) is injected into female Wistar rats. |
| 投薬量 | ≤300 mg/kg | |
| 投与方法 | Administered via i.p. | |
参考
カスタマーフィードバック
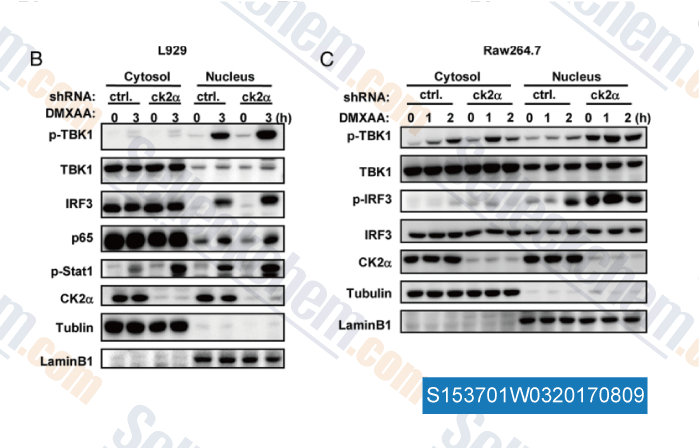
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , J Immunol, 2015, 194:4477-4488]
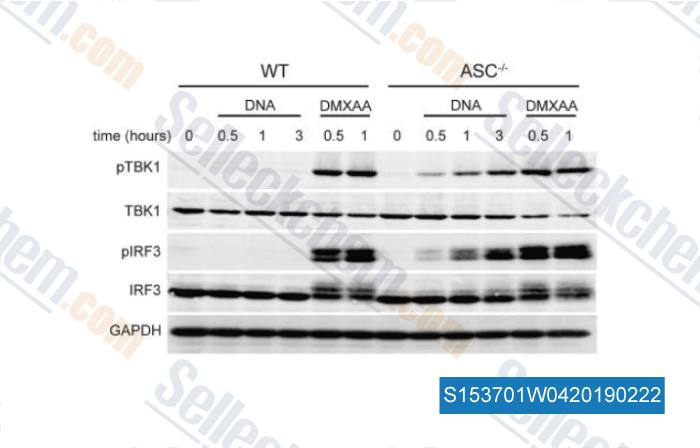
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , J Immunol, 2016, 196(7):3191-8]
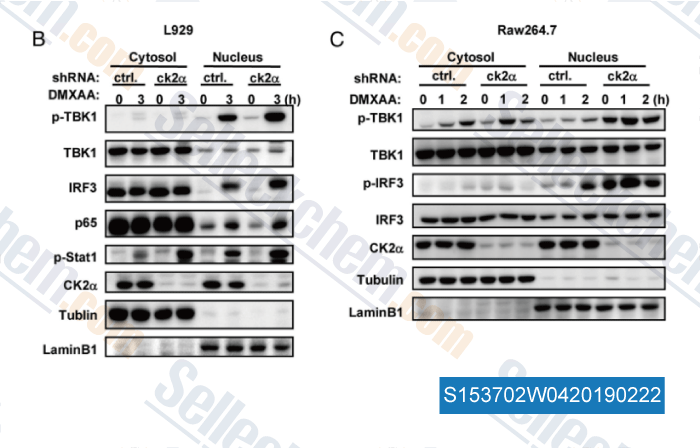
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , J Immunol, 2015, 194(9):4477-88]
Selleckの高級品が、幾つかの出版された研究調査結果(以下を含む)で使われた:
| S-nitrosothiol homeostasis maintained by ADH5 facilitates STING-dependent host defense against pathogens [ Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1):1750] | PubMed: 38409248 |
| Glycolysis drives STING signaling to facilitate dendritic cell antitumor function [ J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(7)e166031] | PubMed: 36821379 |
| Termination of STING responses is mediated via ESCRT-dependent degradation [ EMBO J, 2023, 42(12):e112712] | PubMed: 37139896 |
| Activation of STING by SAMHD1 Deficiency Promotes PANoptosis and Enhances Efficacy of PD-L1 Blockade in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma [ Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(14):4627-4643] | PubMed: 37781035 |
| High glucose-induced STING activation inhibits diabetic wound healing through promoting M1 polarization of macrophages [ Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1):136] | PubMed: 37100799 |
| Activation of STING by SAMHD1 Deficiency Promotes PANoptosis and Enhances Efficacy of PD-L1 Blockade in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma [ Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(14):4627-4643] | PubMed: 37781035 |
| P2rx1 deficiency alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure by regulating the STING signaling pathway [ Cell Biol Toxicol, 2023, 10.1007/s10565-023-09800-1] | PubMed: 37046119 |
| EMSY inhibits homologous recombination repair and the interferon response, promoting lung cancer immune evasion [ Cell, 2022, 185(1):169-183.e19] | PubMed: 34963055 |
| Intercellular transfer of activated STING triggered by RAB22A-mediated non-canonical autophagy promotes antitumor immunity [ Cell Res, 2022, 10.1038/s41422-022-00731-w] | PubMed: 36280710 |
| The volume-regulated anion channel LRRC8C suppresses T cell function by regulating cyclic dinucleotide transport and STING-p53 signaling [ Nat Immunol, 2022, 23(2):287-302] | PubMed: 35105987 |
長期の保管のために-20°Cの下で製品を保ってください。
人間や獣医の診断であるか治療的な使用のためにでない。
各々の製品のための特定の保管と取扱い情報は、製品データシートの上で示されます。大部分のSelleck製品は、推薦された状況の下で安定です。製品は、推薦された保管温度と異なる温度で、時々出荷されます。長期の保管のために必要とされてそれと異なる温度で、多くの製品は、短期もので安定です。品質を維持するが、夜通しの積荷のために最も経済的な貯蔵状況を用いてあなたの送料を保存する状況の下に、製品が出荷されることを、我々は確実とします。製品の受領と同時に、製品データシートの上で貯蔵推薦に従ってください。
