|
受注:045-509-1970 |
技術サポート:[email protected] 平日9:00〜18:00 1営業日以内にご連絡を差し上げます |
化学情報
|
Synonyms | N/A | Storage (From the date of receipt) |
2 years -80°C liquid |
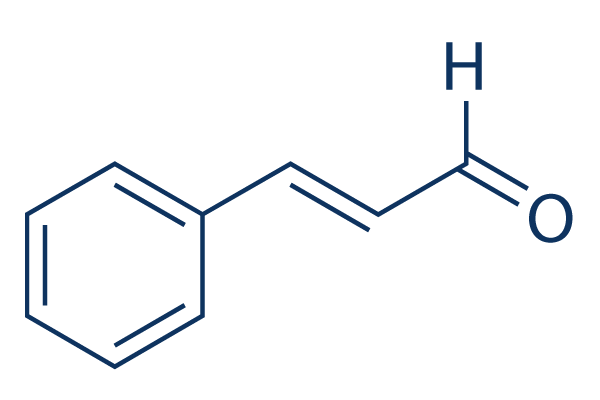
| 化学式 | C9H8O |
|||
| 分子量 | 132.16 | CAS No. | 14371-10-9 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | 体外 | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. |
||||
生物活性
| 製品説明 | Cinnamaldehyde is a flavonoid that is naturally synthesized by the shikimate pathway. Its supplementation can improve glucose and lipid homeostasis in diabetic animals; a TRPA1 agonist. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in vitro | Cinnamaldehyde (40 μM) could enhance the expression of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), and suppress the expression of perilipin and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as well as reduce adipocyte genes expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (CEBP-α) in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. It also increases expression of PPARδ and PPARγ as well as its targeted genes such as aP2 and CD36 in 3T3-L1 differentiated adipocytes. Cinnamaldehyde (40 μM) treatment increases GLUT4 expression via activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and triggering its downstream effector myocyte enhancer factors 2 (MEF2) in C2C12 cells. Its treatment regulates oxidative metabolism through increasing expressions of 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), NAD+-dependent deacetylases sirtuin 1, PGC-1α and cytochrome C as well as improving PPARα and PPARβ/δ expression, which contributes to mitochondrial biogenesis. However, cinnamaldehyde is demonstrated to inhibit mitochondrial metabolism by reducing basal and chemically-induced peak myotube oxidative metabolism in C2C12 cells[1]. Cinnamaldehyde exerts cytotoxic effects on human leukemia K562 cells by inducing apoptosis and synergizing the cytotoxicity of CIK cells against K562 cells[3]. | |||||
| in vivo | Cinnamaldehyde exhibits glucolipid lowering effects in diabetic animals by increasing glucose uptake and improving insulin sensitivity in adipose and skeletal muscle tissues, improving glycogen synthesis in liver, restoring pancreatic islets dysfunction, slowing gastric emptying rates, and improving diabetic renal and brain disorders. Cinnamaldehyde exerts these effects through its action on multiple signaling pathways, including PPARs, AMPK, PI3K/IRS-1, RBP4-GLUT4, and ERK/JNK/p38MAPK, TRPA1-ghrelin and Nrf2 pathways. In addition, cinnamaldehyde seems to regulate the activities of PTP1B and α-amylase. Oral administration of cinnamaldehyde ranging from 20mg/kg to 40 mg/kg per day for a duration lasting from 21 to 60 days results in a significant improvement in the levels of blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) as well as insulin sensitivity in STZ-induced diabetic rats. Cinnamaldehyde is not stable in the body, with the possibility of metabolizing into cinnamic acid and transforming into cinnamyl alcohol. Excessive doses of cinnamaldehyde may generate the toxic response. In human, 3% cinnamaldehyde may cause skin irritation. Cinnamaldehyde is demonstrated to decrease serum IL-1β and inhibit inflammatory gene expression (COX-2, MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-6) in WAT of HFD insulted male Swiss albino mice and C57BLKS db/db mice, while increased expression of Cpt1a protects against pro-inflammatory adipokines release and promotes fatty acid oxidation, which contributes to an improvement in insulin resistance[1]. | |||||
| 密度 | 1.05 g/mL at 25 °C | |||||
プロトコル(参考用のみ)
| 細胞アッセイ | 細胞株 | K562 cells |
|---|---|---|
| 濃度 | 120 or 180 μmol/L | |
| 反応時間 | 4, 9, or 24 h | |
| 実験の流れ | K562 cells are treated with various concentrations of TCA for 4, 9, or 24 h. Cells are harvested and labeled with Annexin V conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (Annexin V-FITC) and PI. The cells are then analyzed by flow cytometry. Apoptotic cells are defined as Annexin V-positive and PI-negative cells (early apoptotic cells) plus Annexin V-positive and PI-positive cells (late apoptotic cells). |
参考
|
Selleckの高級品が、幾つかの出版された研究調査結果(以下を含む)で使われた:
| Activation of TRPA1 in Bladder Suburothelial Myofibroblasts Counteracts TGF-β1-Induced Fibrotic Changes [ Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(11)9501] | PubMed: 37298451 |
| Cinnamic acid inhibits cell viability, invasion, and glycolysis in primary endometrial stromal cells by suppressing NF-κB-induced transcription of PKM2 [ Biosci Rep, 2021, BSR20211828] | PubMed: 34499120 |
長期の保管のために-20°Cの下で製品を保ってください。
人間や獣医の診断であるか治療的な使用のためにでない。
各々の製品のための特定の保管と取扱い情報は、製品データシートの上で示されます。大部分のSelleck製品は、推薦された状況の下で安定です。製品は、推薦された保管温度と異なる温度で、時々出荷されます。長期の保管のために必要とされてそれと異なる温度で、多くの製品は、短期もので安定です。品質を維持するが、夜通しの積荷のために最も経済的な貯蔵状況を用いてあなたの送料を保存する状況の下に、製品が出荷されることを、我々は確実とします。製品の受領と同時に、製品データシートの上で貯蔵推薦に従ってください。
