|
受注:045-509-1970 |
技術サポート:[email protected] 平日9:00〜18:00 1営業日以内にご連絡を差し上げます |
化学情報
|
Synonyms | pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, QUIN | Storage (From the date of receipt) |
3 years -20°C powder 1 years -80°C in solvent |
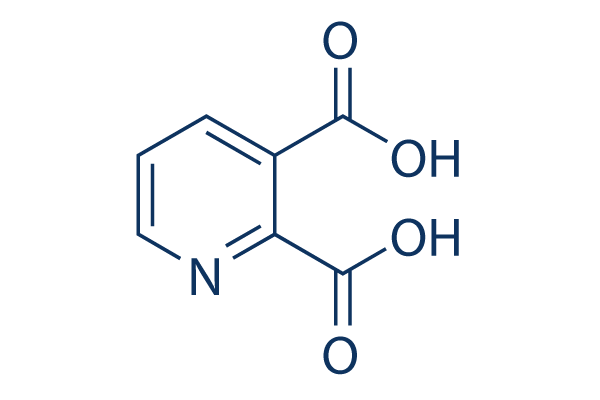
| 化学式 | C7H5NO4 |
|||
| 分子量 | 167.12 | CAS No. | 89-00-9 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | 体外 | DMSO | 25 mg/mL (149.59 mM) | |
| Water | 3 mg/mL (17.95 mM) | |||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. |
||||
溶剤液(一定の濃度)を調合する
生物活性
| 製品説明 | Quinolinic Acid (pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, QUIN), a neuroactive metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, is an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. |
|---|---|
| in vitro | QUIN is an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, and it has a high in vivo potency as an excitotoxin. Although QUIN has an uptake system, its neuronal degradation enzyme is rapidly saturated, and the rest of extracellular QUIN can continue stimulating the NMDA receptor. QUIN (10 μM) prevents of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule neurons, nevertheless mature organotypic cultures of rat corticostriatal system or caudate nucleus chronically exposed to 100 nM QUIN for up to 7 weeks show focal degeneration characterized by the presence of vacuoles in neuropil, swollen dendrites, occasional swollen post-synaptic elements, and degenerated neurons. In vitro QUIN treatment of human primary foetal neurons leads to a substantial increase of tau phosphorylation at multiple positions. The increase in QUIN-induced phosphorylation of tau is attributed to a decrease in the expression and activity of the major tau phosphatases. QUIN can inhibit B monoamine oxidase (MAO-B) in human brain synaptosomal mitochondria and also can be a potent inhibitor of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (EC 4.1.1.32) from rat liver cytoplasm, an important enzyme in the gluconeogenesis pathway that converts oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate. QUIN can increase free radical production by inducing NOS activity in astrocytes and neurons, leading to oxidative stress, increasing both poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activity and extracellular lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity[1]. |
| in vivo | Quinolinic acid (QUIN), a neuroactive metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, is normally presented in nanomolar concentrations in human brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is often implicated in the pathogenesis of a variety of human neurological diseases. The concentration of QUIN varies among different brain regions, with the cerebral cortex containing approximately 1.8 nmol/g wet weight; almost 2-fold than that found in the hippocampus (1 nmol/g wet weight). Intraarterial administration of either micromolar or millimolar concentrations of QUIN results in only negligible accumulations of this metabolite in the brain, suggesting that the central nervous system (CNS) appears to be well protected by the blood brain barrier (BBB) from peripheral QUIN. QUIN can also increase glutamate release and inhibit its reuptake by astrocytes, thus increasing its concentration in the microenvironments, causing neurotoxicity and also limiting glutamate to glutamine recycling in astrocytes by decreasing glutamine synthetase activity. Intrastriatal injection of QUIN provokes a decrease of cellular respiration and ATP levels[1]. |
プロトコル(参考用のみ)
| 動物実験 | 動物モデル | C57Bl/6J mice |
|---|---|---|
| 投薬量 | 30 nmol | |
| 投与方法 | Intracerebral injection |
参考
|
長期の保管のために-20°Cの下で製品を保ってください。
人間や獣医の診断であるか治療的な使用のためにでない。
各々の製品のための特定の保管と取扱い情報は、製品データシートの上で示されます。大部分のSelleck製品は、推薦された状況の下で安定です。製品は、推薦された保管温度と異なる温度で、時々出荷されます。長期の保管のために必要とされてそれと異なる温度で、多くの製品は、短期もので安定です。品質を維持するが、夜通しの積荷のために最も経済的な貯蔵状況を用いてあなたの送料を保存する状況の下に、製品が出荷されることを、我々は確実とします。製品の受領と同時に、製品データシートの上で貯蔵推薦に従ってください。
