- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
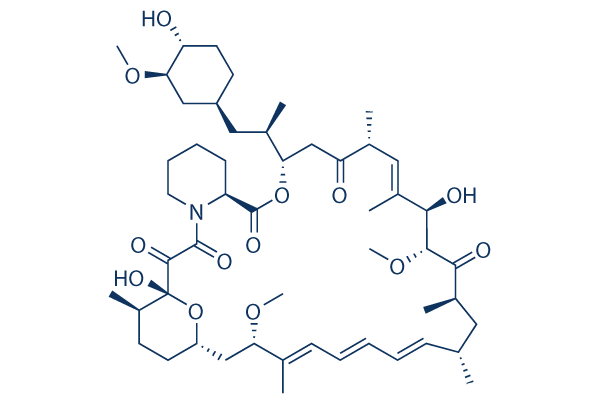
Rapamycin (Sirolimus)
別名:Sirolimus, AY-22989, NSC-2260804
ラパマイシン (Rapamycin (NSC-2260804,AY-22989)) は特異的 mTOR 阻害剤であり、HEK293 細胞に対する IC50 は < 0.1 nM です。
CAS No. 53123-88-9
文献中Selleckの製品使用例(1852)
製品安全説明書
現在のバッチを見る:
純度:
99.63%
99.63
Rapamycin (Sirolimus)と併用されることが多い化合物
Imidazole Ketone Erastin (IKE)
It and Imidazole ketone erastin induce cell death in ALL cell lines, resulting in a longer survival time for xenograft mice with ALL.
This compound and MG132 combination synergize the apoptotic and autophagic effects of curcumol in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Combined use of this compound reduces photoreceptor necrosis and preserve the ONL thickness after retinal detachment.
Rapamycin (Sirolimus)関連製品
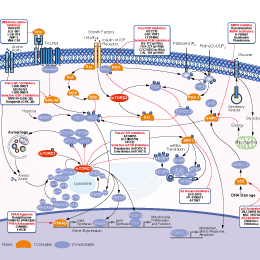
シグナル伝達経路
mTOR阻害剤の選択性比較
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | 活性情報 | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U937 | Antibacterial Assay | 50 μM | 48 h | Induces antibacterial activity against wild type Legionella pneumophila Philadelphia-1 JR32 in U937 cells | 21142106 |
| HEK293 cells | Kinase Assay | 50 nM | 45 min | Inhibits mTOR kinase activity with IC50 of 0.1 nM | 17350953 |
| MCF-7 | Autophagy Assay | 30 nM | 4 h | Induces autophagy | 20028134 |
| PC3 | Kinase Assay | 100 nM | 1 h | Potently inhibits mTOR-mediated S6 phosphorylation with IC50 of <10 nM. | 21978683 |
| HeLa | Function Assay | 100 nM | 36 h | Induces FRB K2095P, T2098L, W2101F mutant-ubiquitinC interaction | 17563385 |
| SYF | Function Assay | 100 nM | 24 h | Induces FRB-FKBP complex interaction | 17563385 |
| HEK293 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 8 h | Inhibits TPA-induced degradation of Pdcd4 with EC50 of 50 nM | 21539301 |
| Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells transfected with N-luc and C-luc | Function Assay | 100 nM | 4 h | Induces luciferase protein trans-splicing in Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells transfected with N-luc and C-luc | 17128262 |
| cells from the thymus of normal BALB/c mice | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 nM | 72 h | Inhibits lymphoproliferation (LAF) with IC50 of 3 nM | 10021948 |
| HT-29 | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 nM | 72 h | Potentiates digitoxin-induced cytotoxicity | 24900873 |
| PC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1.5 μM | 1 h | Induces antiproliferative activity against human PC3 cells with IC50 of <10 nM | 21978683 |
| U87MG | Kinase Assay | 1 μM | 6 h | Potently inhibits mTOR-mediated S6 phosphorylation | 19848404 |
| PBMC | Function Assay | 1 nM | 14 d | Reduces CCR5 density | 17485501 |
| HEK293T | Antiviral Assay | 1 nM | 4 d | Induces antiviral activity against HIV1 X4 with EC50 of 0.3 nM | 17485501 |
| COS7 cells expressing EGFP-HDQ74/rheb | Autophagy Assay | 0.2 μM | 24 h | Induces autophagy | 18391949 |
| COS7 cells expressing EGFP-LC3 | Autophagy Assay | 0.2 μM | 24 h | Induces autophagy | 18391949 |
| H4 | Function Assay | 0.2 μM | 24 h | Increases the ratio of light chain 3 subunit 2 to light chain 3 subunit 1 in human H4 cells | 18024584 |
| Lewis rat lymph node cells | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 μM | IC50=2.6 μM | 16185865 | |
| Human mixed lymphocyte | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5 nM | IC50=1.6 nM. | 16185865 | |
| BT-20 | Kinase Assay | 20 μM | Does not inhibit mTORC2 dependent pAkT S473 phosphorylation | 21353551 | |
| 他の多くの細胞株試験データをご覧になる場合はこちらをクリックして下さい | |||||
生物活性
| 製品説明 | ラパマイシン (Rapamycin (NSC-2260804,AY-22989)) は特異的 mTOR 阻害剤であり、HEK293 細胞に対する IC50 は < 0.1 nM です。 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In Vitro | ||||
| In vitro |
Rapamycin inhibits endogenous mTOR activity in HEK293 cells with IC50 of ~0.1 nM, more potently than iRap and AP21967 with IC50 of ~5 nM and ~10 nM, respectively. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, this compound treatment induces a severe G1/S cell cycle arrest and inhibition of translation initiation to levels below 20% of control. It significantly inhibits the cell viability of T98G and U87-MG in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 of 2 nM and 1 μM, respectively, while displaying little activity against U373-MG cells with IC50 of >25 μM despite the similar extent of the inhibition of mTOR signaling. This chemical (100 nM) induces G1 arrest and autophagy but not apoptosis in Rapamycin-sensitive U87-MG and T98G cells by inhibiting the function of mTOR. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | Immunoblotting for the mTOR kinase assay | |||
| HEK293 cells are plated at 2-2.5×105 cells/well of a 12-well plate and serum-starved for 24 hours in DMEM. Cells are treated with increasing concentrations of Rapamycin (0.05-50 nM) for 15 minutes at 37 °C. Serum is added to a final concentration of 20% for 30 minutes at 37 °C. Cells are lysed, and cell lysates are separated by SDS-PAGE. Resolved proteins are transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane and immunoblotted with a phosphospecific primary antibody against Thr-389 of p70 S6 kinase. Data are analyzed using ImageQuant and KaleidaGr | ||||
| 細胞実験 | 細胞株 | U87-MG, T98G, and U373-MG | ||
| 濃度 | Dissolved in DMSO, final concentrations ~25 μM | |||
| 反応時間 | 72 hours | |||
| 実験の流れ | Cells are exposed to various concentrations of Rapamycin for 72 hours. For the assessment of cell viability, cells are collected by trypsinization, stained with trypan blue, and the viable cells in each well are counted. For the determination of cell cycle, cells are trypsinized, fixed with 70% ethanol, and stained with propidium iodide using a flow cytometry reagent set. Samples are analyzed for DNA content using a FACScan flow cytometer and CellQuest software. For apoptosis detection, cells are stained with the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) technique using an ApopTag apoptosis detection kit. To detect the development of acidic vesicular organelles (AVO), cells are stained with acridine orange (1 μg/mL) for 15 minutes, and examined under a fluorescence microscope. To quantify the development of AVOs, cells are stained with acridine orange (1 μg/mL) for 15 minutes, removed from the plate with trypsin-EDTA, and analyzed using the FACScan flow cytometer and CellQuest software. To analyze the autophagic process, cells are incubated for 10 minutes with 0.05 mM monodansylcadaverine at 37 °C and are then observed under a fluorescence microscope. |
|||
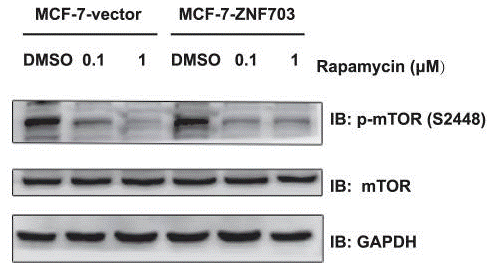
| 実験結果図 | Methods | Biomarkers | 結果図 | PMID |
| Western blot | p-mTOR(S2448)/mTOR |
|
23991038 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell proliferation |
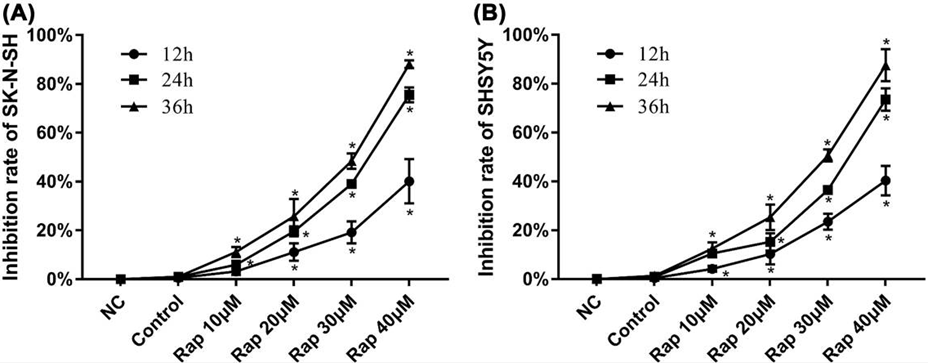
|
30393233 | |
| Histomorphology | Haematoxylin & Eosin |
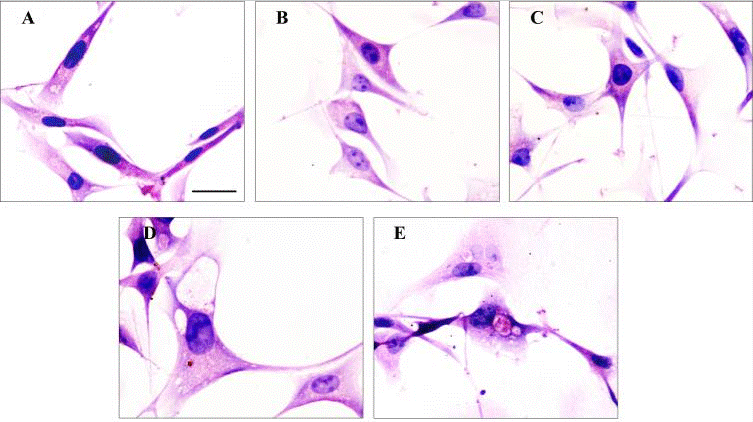
|
28418837 | |
| Immunofluorescence | NeuN p62/Beclin |
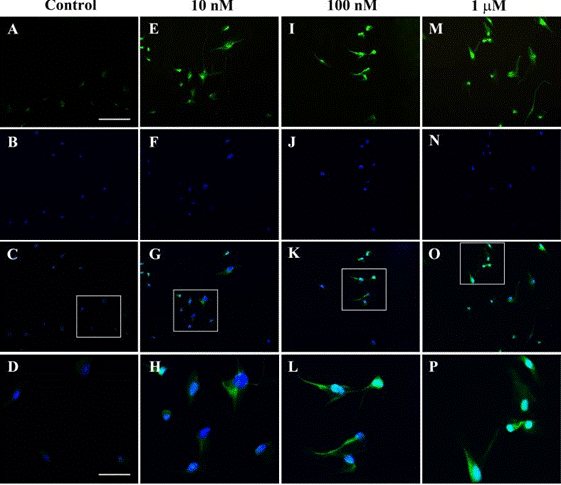
|
28418837 | |
| ELISA | Type III collagen/Fibronectin |
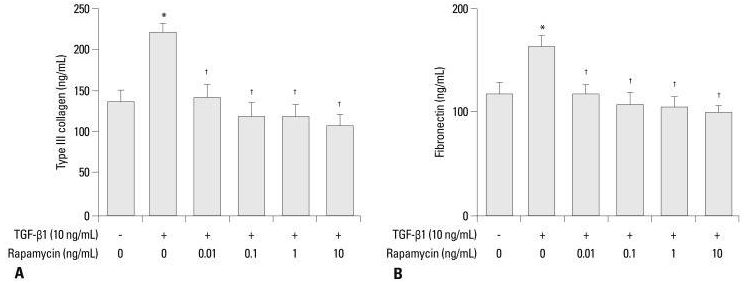
|
23364979 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In Vivo |
Treatment with Rapamycin in vivo specifically blocks targets known to be downstream of mTOR such as the phosphorylation and activation of p70S6K and the release of inhibition of eIF4E by PHAS-1/4E-BP1, leading to complete blockage of the hypertrophic increases in plantaris muscle weight and fibre size. Short-term treatment with this compound, even at the lowest dose of 0.16 mg/kg, produces profound inhibition of p70S6K activity, which correlates with increased tumor cell death and necrosis of the Eker renal tumors. This chemical inhibits metastatic tumor growth and angiogenesis in CT-26 xenograft models by reducing the production of VEGF and blockage of VEGF-induced endothelial cell signaling. Treatment with this compound at 4 mg/kg/day significantly reduces tumor growth of C6 xenografts, and tumor vascular permeability. |
|
|---|---|---|
| 動物実験 | 動物モデル | Athymic Nu/Nu mice inoculated subcutaneously with VEGF-A-expressing C6 rat glioma cells |
| 投与量 | ~4 mg/kg/day | |
| 投与経路 | Injection i.p. | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06308445 | Not yet recruiting | Familial Adenomatous Polyposis |
University Hospital Toulouse |
August 1 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06310291 | Not yet recruiting | Celiac Disease |
Barinthus Biotherapeutics |
April 2024 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT06091332 | Not yet recruiting | Cavernous Malformations|Brain Stem Hemorrhage |
Huashan Hospital |
December 1 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05997056 | Recruiting | Neuroendocrine Tumors|NET|Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor|Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumor|Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumor |
Aadi Bioscience Inc. |
November 7 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06022068 | Enrolling by invitation | Alzheimer Disease |
Karolinska Institutet|Karolinska University Hospital |
September 1 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT04989686 | Recruiting | Immunosuppression |
Children''s Hospital of Philadelphia|Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) |
June 8 2023 | -- |
|
化学情報
| 分子量 | 914.18 | 化学式 | C51H79NO13 |
| CAS No. | 53123-88-9 | SDF | Download Rapamycin (Sirolimus) SDFをダウンロードする |
| Smiles | CC1CCC2CC(C(=CC=CC=CC(CC(C(=O)C(C(C(=CC(C(=O)CC(OC(=O)C3CCCCN3C(=O)C(=O)C1(O2)O)C(C)CC4CCC(C(C4)OC)O)C)C)O)OC)C)C)C)OC | ||
| 保管 | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 100 mg/mL ( (109.38 mM); 吸湿したDMSOは溶解度を減少させます。新しいDMSOをご使用ください。) Ethanol : 25 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
モル濃度計算器 |
|
in vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
投与溶液組成計算機 | |||||
実験計算
投与溶液組成計算機(クリア溶液)
ステップ1:実験データを入力してください。(実験操作によるロスを考慮し、動物数を1匹分多くして計算・調製することを推奨します)
mg/kg
g
μL
匹
ステップ2:投与溶媒の組成を入力してください。(ロット毎に適した溶解組成が異なる場合があります。詳細については弊社までお問い合わせください)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
計算結果:
投与溶媒濃度: mg/ml;
DMSOストック溶液調製方法: mg 試薬を μL DMSOに溶解する(濃度 mg/mL, 注:濃度が当該ロットのDMSO溶解度を超える場合はご連絡ください。 )
投与溶媒調製方法:Take μL DMSOストック溶液に μL PEG300,を加え、完全溶解後μL Tween 80,を加えて完全溶解させた後 μL ddH2O,を加え完全に溶解させます。
投与溶媒調製方法:μL DMSOストック溶液に μL Corn oil,を加え、完全溶解。
注意:1.ストック溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことをご確認ください;
2.順番通りに溶剤を加えてください。次のステップに進む前に溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことを確認してから加えてください。ボルテックス、ソニケーション、水浴加熱など物理的な方法で溶解を早めることは可能です。
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須