- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
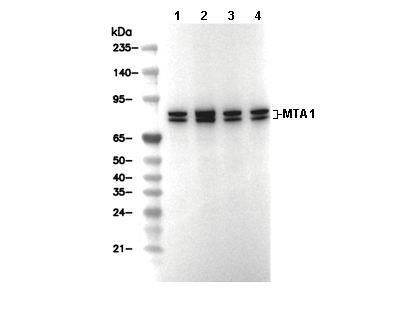
MTA1 Antibody [F4J14]
Catalog No.: F4782
Application:
Reactivity:
当該製品は品切れ状态で、ごメールアドレスを教えていただければ、在庫があると、メールで顧客様に伝えます。
代表番号: 045-509-1970|電子メール:sales@selleck.co.jp
使用情報
| Dilution |
|---|
|
| Application |
|---|
| WB, IF, FCM |
| Source |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Reactivity |
|---|
| Human |
| Storage Buffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Storage (from the date of receipt) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Predicted MW Observed MW |
|---|
| 81 kDa 78-82 kDa, 85 kDa |
| *なぜ予測分子量と実際の分子量が異なるのか? 下記の原因により、実際の分子量が予測と異なる:タンパク質の翻訳後修飾(リン酸化/糖鎖付加),スプライシングバリアント,イソフォーム,相対的な電荷,ポリマー。 |
| ポジティブコントロール | HeLa cell; A549 cell; HEK-293 cell; 293T cell; MCF7 cell |
|---|---|
| ネガティブコントロール |
プロトコール
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 120 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
| IF |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample Preparation
1. Adherent Cells: Place a clean, sterile coverslip in a culture dish. Once the cells grow to near confluence as a monolayer, remove the coverslip for further use.
2. Suspension Cells: Seed the cells onto a clean, sterile slide coated with poly-L-lysine.
3. Frozen Sections: Allow the slide to thaw at room temperature. Wash it with pure water or PBS for 2 times, 3 minutes each time.
4. Paraffin Sections: Deparaffinization and rehydration. Wash the slide with pure water or PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time. Then perform antigen retrieval.
Fixation
1. Fix the cell coverslips/spots or tissue sections at room temperature using a fixative such as 4% paraformaldehyde (4% PFA) for 10-15 minutes.
2. Wash the sample with PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time.
Permeabilization
1.Add a detergent such as 0.1–0.3% Triton X-100 to the sample and incubate at room temperature for 10–20 minutes.
(Note: This step is only required for intracellular antigens. For antigens expressed on the cell membrane, this step is unnecessary.)
Wash the sample with PBS for 3 times, 3 minutes each time.
Blocking
Add blocking solution and incubate at room temperature for at least 1 hour. (Common blocking solutions include: serum from the same source as the secondary antibody, BSA, or goat serum.)
Note: Ensure the sample remains moist during and after the blocking step to prevent drying, which can lead to high background.
Immunofluorescence Staining (Day 1)
1. Remove the blocking solution and add the diluted primary antibody.
2. Incubate the sample in a humidified chamber at 4°C overnight.
Immunofluorescence Staining (Day 2)
1. Remove the primary antibody and wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
2. Add the diluted fluorescent secondary antibody and incubate in the dark at 4°C for 1–2 hours.
3. Remove the secondary antibody and wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
4. Add diluted DAPI and incubate at room temperature in the dark for 5–10 minutes.
5. Wash with PBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Mounting
1. Mount the sample with an anti-fade mounting medium.
2. Allow the slide to dry at room temperature overnight in the dark.
3. Store the slide in a slide storage box at 4°C, protected from light.
|
生物学的記述
| Specificity |
|---|
| MTA1 Antibody [F4J14] detects endogenous levels of total MTA1 protein. |
| タンパク質の局在 |
|---|
| 細胞質、細胞核、細胞骨格 |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| Q13330 |
| Clone |
|---|
| F4J14 |
| Synonym(s) |
|---|
| Metastasis-associated protein MTA1; MTA1 |
| Background |
|---|
| MTA1 (Metastasis-Associated Protein 1) is an essential scaffold component of the Nucleosome Remodeling and Deacetylase (NuRD) complex, a chromatin-modifying corepressor belonging to the metastasis-associated (MTA) family of transcriptional regulators. MTA1 features conserved domains, including an N-terminal BAH domain forming a β-barrel core with insertions for histone H4 recognition, a central zinc-finger motif (C2HC), the ELM2 domain with a basic pocket for HDAC1 activation via helix 3 of the adjacent SANT domain, and a C-terminal KRAARR motif modulating RBBP4 binding; intrinsically disordered regions become ordered upon interaction to stabilize NuRD assembly. MTA1 facilitates NuRD-mediated histone deacetylation and nucleosome remodeling by directly contacting HDACs, RBBP4/7, and Mi-2, enabling recruitment to gene loci for epigenetic silencing. Functionally, it activates class I HDACs through inositol phosphate binding at the ELM2-SANT interface, regulates mitosis by binding transcripts at splicing motifs to control alternative splicing of regulators like ATRX and MYBL2, and influences SAC components (e.g., MAD1/2) for proper chromosome segregation. MTA1 deletion causes defective mitotic arrest, chromosomal instability, and tumorigenesis, with overexpression linked to cancer progression via hypoxia-induced HIF-1α stabilization and Wnt/β-catenin modulation. |
| References |
|---|
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須