- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
Tivantinib
別名:ARQ 197
チバンチニブは、細胞を含まないアッセイで0.355 μMのKiを持ち、Ronへの活性はほとんどなく、EGFR、InsR、PDGFRα、またはFGFR1/4への阻害作用がない最初の非ATP競合的c-Met阻害剤です。チバンチニブ (ARQ 197) はG2/M期停止とapoptosisを誘導します。
CAS No. 905854-02-6
文献中Selleckの製品使用例(49)
製品安全説明書
現在のバッチを見る:
純度:
99.65%
99.65
Tivantinib関連製品
シグナル伝達経路
c-Met阻害剤の選択性比較
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | 活性情報 | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNK-45 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | ||
| HT29 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | ||
| NCI-H441 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | inhibits c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways | ||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50>33 μM | ||
| NCI-H661 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50>33 μM | ||
| NCI-H446 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=7 μM | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.55 μM | ||
| DLD-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.53 μM | ||
| A549 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.59 μM | ||
| SK-OV-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.66 μM | ||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.6 μM | ||
| A375 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.42 μM | ||
| NCI-H441 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.3 μM | ||
| HT29 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.49 μM | ||
| MKN-45 | Growth inhibitory assay | 33 μM | IC50=0.58 μM | ||
| HT29 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | significantly induces apoptosis by 80-90%. | ||
| MKN-45 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | significantly induces apoptosis by 80-90%. | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Apoptosis assay | ~10 μM | modestly induces apoptosis by 35%. | ||
| MDA-MB-231/TGL | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | GI50=1.2 μM | ||
| 1833/TGL | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | GI50=3.7 μM | ||
| EBC1 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | inhibits the cell growth. | ||
| SNU638 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | inhibits the cell growth. | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | ||
| H460 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | ||
| HCC827 | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | not affect | ||
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | disrupts microtubule | ||
| EBC1 | Function assay | 10 μM | disrupts microtubule | ||
| H460 | Function assay | 10 μM | inhibits tubulin polymerization | ||
| K562/VCR | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | shows cytotoxic activity | ||
| CEM/VBL | Cytotoxic assay | ~10 μM | shows cytotoxic activity | ||
| U266 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.1 μM | ||
| OPM-2 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.8 μM | ||
| MM.1S | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=1.6 μM | ||
| MM.1R | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 49% | ||
| RPMI-8226 | Cytotoxic assay | ~3 μM | IC50=0.9 μM | ||
| ANBL-6 | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | ||
| ANLB-6/V10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | ||
| KAS-6/1 | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | ||
| KAS-6/V10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | ||
| KAS-6/R10R | Cytotoxic assay | 1 μM | induces cell death by more than 50% | ||
| 8226/S | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 54% | ||
| 8226/LR-5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 3 μM | inhibits cell growth by 54% | ||
| Huh7 | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | IC50=9.9 nM | ||
| Hep3B | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | IC50=448.7 nM | ||
| HepG2 | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | IC50=139.77 nM | ||
| Chang | Cytotoxic assay | ~4.8 μM | IC50=448.7 nM | ||
| Huh7 | Function assay | 1.6 μM | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| Hep3B | Function assay | 1.6 μM | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| HepG2 | Function assay | 1.6 μM | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| Chang | Function assay | 1.6 μM | causes a G2/M cell cycle arrest | ||
| MHCC97L | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | IC50=315 nM | ||
| MHCC97H | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | IC50=368 nM | ||
| Huh7 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | IC50=265 nM | ||
| HepG2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | IC50=392 nM | ||
| MHCC97L | Function assay | 1 μM | induces microtubules depolymerization | ||
| Huh7 | Function assay | 1 μM | induces microtubules depolymerization | ||
| MHCC97L | Apoptosis assay | 1 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| Huh7 | Apoptosis assay | 1 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| C3H 10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts | Kinase assay | 25 μM | reduces Histone H3 and H4 acetylation levels | ||
| H23 | Growth inhibitory assay | 25 μM | significantly inhibits cell growth. | ||
| WM35 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | significantly inhibits cell growth. | ||
| NIH 3T3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| H838 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| H1395 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | does not have a significant inhibitory effect | ||
| Quiescent S2 | Kinase assay | 30 μM | completely abrogates TSA-induced hyperacetylation of H3K4me3 histones | ||
| PC3 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| Du145 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| LNCaP | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| LAPC-4 | Apoptosis assay | 20 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| LNCaP | Function assay | 20 μM | decreases PSA secretion and p65 expression levels | ||
| LAPC-4 | Function assay | 20 μM | decreases PSA secretion and p65 expression levels | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~50 μM | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| SKNO-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~50 μM | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | reduces expression of acetylated histone H3, c-kit and bcl-2 | ||
| SKNO-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | reduces expression of acetylated histone H3, c-kit and bcl-2 | ||
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | enhances mitotic catastrophe | ||
| NRK-52E | Function assay | 10 μM | inhibits Ang II-induced STAT3 nuclear translocation and the expression of TGF-β1, collagen IV and fibronectin | ||
| PC12 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~12.5 μM | prevents TSA-induced neurite formation | ||
| A549 | Function assay | ~50 μM | affects the viral life cycle and host response | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | ~30 μM | reduces pro-inflammatory gene expression | ||
| MEMM | Kinase assay | 15 µM | decreases acetylation of histone H3 | ||
| MEMM | Growth inhibitory assay | ~20 µM | inhibits cell proliferation | ||
| MEMM | Apoptosis assay | 15 µM | induces the presence of the apoptosis protein, cleaved Caspase-3 | ||
| T47D | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=72 nM | ||
| ZR-75-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=79 nM | ||
| BT474 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=86 nM | ||
| HCC1954 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=119 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-453 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=975 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=3208 nM | ||
| SkBr3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| HCT116 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=5836 nM | ||
| HT29 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| HFF | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=7615 nM | ||
| HN5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| 786-0 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=4009 nM | ||
| H157 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2642 nM | ||
| NCI-H460 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>2,500 nM | ||
| SKOV-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2126 nM | ||
| OVCAR-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2918 nM | ||
| BXPC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=3141 nM | ||
| MiaPaCa | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=5433 nM | ||
| PANC-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=8681 nM | ||
| LNCaP | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=147 nM | ||
| DU145 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=3812 nM | ||
| PC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10,000 nM | ||
| BT474 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 160 nM | ||
| 786-0 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 150 nM | ||
| LNCaP | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 43 nM | ||
| PC3 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits pGSK3β with IC50 of 49 nM | ||
| KARPAS-231 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=41 nM | ||
| CCRFSB | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=155 nM | ||
| SUP B15 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=197 nM | ||
| SD-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=320 nM | ||
| RS4;11 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=654 nM | ||
| MN-60 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=3602 nM | ||
| Tanoue | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=4517 nM | ||
| RCH-ACV | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=152 nM | ||
| SEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=202 nM | ||
| KASUMI-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=225 nM | ||
| REH | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=288 nM | ||
| 697 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=338 nM | ||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=421 nM | ||
| MHH-CALL–3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=812 nM | ||
| MHH-CALL–2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=2114 nM | ||
| J.GAMMA-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=65 nM | ||
| JR45.01 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=68 nM | ||
| A3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=69 nM | ||
| I 2.1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=73 nM | ||
| MOLT-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=74 nM | ||
| P116 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=78 nM | ||
| J.Cam1.6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=79 nM | ||
| I 9.2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=80 nM | ||
| LOUCY | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=117 nM | ||
| J.RT3-T3.5 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=123 nM | ||
| 800000 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=163 nM | ||
| Jurkat | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=225 nM | ||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=232 nM | ||
| Molt-16 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=241 nM | ||
| CEM/C3 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=257 nM | ||
| CEM/C2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=271 nM | ||
| CCRFCEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=327 nM | ||
| CEM/C1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=382 nM | ||
| SUPTI[VB] | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=619 nM | ||
| CCRF–HSB-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | EC50=2117 nM | ||
| I 2.1 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| I 9.2 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| A3 | Apoptosis assay | 10 μM | induces apoptosis | ||
| RD | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | ||
| Rh41 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=33.8 nM | ||
| Rh18 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=303 nM | ||
| Rh30 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=4.81 μM | ||
| BT-12 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | ||
| CHLA-266 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=1.22 μM | ||
| TC-71 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2.52 μM | ||
| CHLA-9 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=591 nM | ||
| CHLA-10 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=102 nM | ||
| CHLA-258 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=1.05 μM | ||
| GBM2 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=9.15 μM | ||
| NB-1643 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=5.4 μM | ||
| NB-Ebc1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | ||
| CHLA-90 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | ||
| CHLA-136 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50>10 μM | ||
| NALM-6 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=265 nM | ||
| COG-LL-317 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=6.49 nM | ||
| RS4;11 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=147 nM | ||
| MOLT-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=40 nM | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=268 nM | ||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=107 nM | ||
| Karpas-299 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=2.93 μM | ||
| Ramos-RA1 | Growth inhibitory assay | 10 μM | IC50=7.35 μM | ||
| H1299 | Kinase assay | 10 μM | inhibits IKBKE-induced Akt Activation | ||
| HPMCs | Function assay | reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human peritoneal mesothelial cells | |||
| 他の多くの細胞株試験データをご覧になる場合はこちらをクリックして下さい | |||||
生物活性
| 製品説明 | チバンチニブは、細胞を含まないアッセイで0.355 μMのKiを持ち、Ronへの活性はほとんどなく、EGFR、InsR、PDGFRα、またはFGFR1/4への阻害作用がない最初の非ATP競合的c-Met阻害剤です。チバンチニブ (ARQ 197) はG2/M期停止とapoptosisを誘導します。 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 特性 | The first selective c-Met inhibitor to be advanced into human clinical trials. | ||
| Targets |
|
| In Vitro | ||||
| In vitro |
ARQ-197 has been shown to prevent HGF/c-met induced cellular responses in vitro. This compound possesses antitumor activity; inhibiting proliferation of A549, DBTRG and NCI-H441 cells with IC50 of 0.38, 0.45, 0.29 μM. Treatment with this agent results in a decrease in phosphorylation of the MAPK signaling cascade and prevention of invasion and migration. In addition, ectopic expression of c-Met in NCI-H661, a cell line having no endogenous expression of c-Met, causes it to acquire an invasive phenotype that is also suppressed by this chemical. Although the addition of increasing concentrations of this inhibitor does not significantly affect the Km of ATP, exposure of c-Met to 0.5 μM of this substance decreased the Vmax of c-Met by approximately 3-fold. The ability of this molecule to decrease the Vmax without affecting the Km of ATP confirmed that it inhibits c-Met through a non–ATP-competitive mechanism and may therefore account for its high degree of kinase selectivity. It prevents human recombinant c-Met with a calculated inhibitory constant Ki of approximately 355 nM. Although the highest concentration of ATP used is 200 μM, the potency of this compound against c-Met is not reduced by using concentrations of ATP up to 1 mM. It blocks c-Met phosphorylation and downstream c-Met signaling pathways. This chemical suppresses constitutive and ligand-mediated c-Met autophosphorylation and, by extension, c-Met activity, in turn leading to the inhibition of downstream c-Met effectors. Its induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis is increased in c-Met–expressing human cancer cells including HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | c-Met SDS-PAGE in vitro kinase assay | |||
| Recombinant c-Met protein (100 ng) is preincubated with increasing concentrations of this compound for 30 minutes at room temperature. Following preincubation, 100 μM of poly-Glu-Tyr substrate and various concentrations of ATP containing 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP are added to the reaction mixture. The reaction is incubated for 5 minutes at room temperature and then stopped by the addition of 5 μL of SDS-polyacrylamide gel, reducing sample buffer. The samples are then loaded onto a 7.5% acrylamide gel and SDS-PAGE is performed. The phosphorylated poly-Glu-Tyr substrates are ultimately visualized by autoradiography. c-Met activity is quantified by densitometry. | ||||
| 細胞実験 | 細胞株 | T29, MKN-45 and MDA-MB-231 cells | ||
| 濃度 | 0.03-10 μM | |||
| 反応時間 | 24, 32, and 48 hours | |||
| 実験の流れ | HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells are seeded in black 96-well plates at 5 × 103 cells per well overnight in a medium with 10% FBS. The next day, cells are treated with increasing concentrations of this compound (0.03-10 μM) for 24, 32, and 48 hours at 37 °C. After this compound treatment, the drug-containing medium is removed and cells are incubated for at least 10 minutes in a labeling solution (10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl, and 6 mM CaCl2) containing 2 μg/mL Hoescht 33342 (blue channel), 500-times diluted Annexin V-FITC (green channel), and 1 μg/mL propidium iodide (red channel). High-content image acquisition and analysis are carried out. The program is set to take four images per well. The exposure time is set at 16.7 ms/10% gain, 500 ms/35% gain, and 300 ms/30% gain for the 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, FITC, and rhodamine channels, respectively. Images are processed and the numbers of positive cells for each channel and each condition are determined. In addition, HT29 cells are treated with increasing concentrations of this compound for 32 hours in the absence or the presence of 25, 50, and 100 μM ZvAD-FMK (irreversible general caspase inhibitor), and the same procedures are undertaken. All experiments are done in triplicate. To determine whether the apoptotic effect is due to c-Met inhibition, the effect of this compound when glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and c-Met are knocked down using siRNA is investigated. HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells are transfected with a nontargeted control siRNA, a gapgh-targeted control siRNA, or a met-targeted siRNA. After 3 days, c-Met, GAPDH, and β-actin expression levels are determined using specific antibodies. To determine if the effect is caspase dependent, HT29, MKN-45, and MDA-MB-231 cells are transfected with a met-targeted siRNA for 2 days and incubated in the absence or the presence of increasing concentrations of ZvAD-FMK for 1 additional day. A nontargeted siRNA and a gapgh-targeted siRNA (siRNA GAPDH) are also transfected in parallel, as controls. Cells are then stained with Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide, and the percentage of apoptotic cells is determined. |
|||
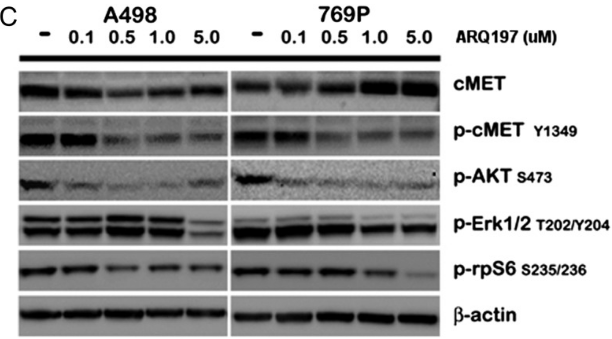
| 実験結果図 | Methods | Biomarkers | 結果図 | PMID |
| Western blot | cMET / p-cMET / p-AKT / p-ERK / p-rpS6 |
|
23022995 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
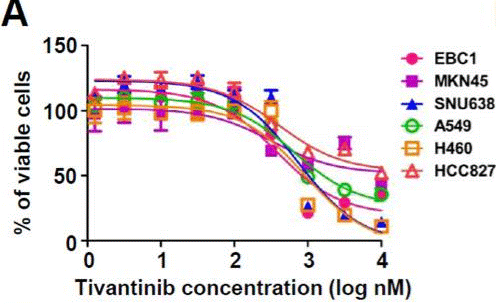
|
23598276 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In Vivo |
All three xenograft models treated with Tivantinib display reductions in tumor growth: 66% in the HT29 model, 45% in the MKN-45 model, and 79% in the MDA-MB-231 model. In these xenograft studies, no significant body weight changes following oral administration of this compound at 200 mg/kg are observed. Pharmacodynamically, the phosphorylation of c-Met in human colon xenograft tumors (HT29) is strongly inhibited by this chemical, as assessed by a dramatic reduction of c-Met autophosphorylation 24 hours after a single oral dose of 200 mg/kg of this agent. This same dosage in mice exhibits that tumor xenografts are exposed to sustained plasma levels of the compound, consistent with the observed pharmacodynamic inhibition of c-Met phosphorylation and inhibition of proliferation of c-Met harboring cancer cell lines. Plasma levels of the agent 10 hours after dosing are determined to be 1.3 μM, more than 3-fold above the biochemical inhibitory constant of this substance for c-Met. Therefore, it is able to suppress its target in vivo in the xenografted human tumor tissue. In conclusion, this inhibitor blocks the growth of c-Met-dependent xenografted human tumors. |
|
|---|---|---|
| 動物実験 | 動物モデル | Female athymic nude mice bearing HT29, MKN-45, or MDA-MB-231 tumor xenografts |
| 投与量 | 200 mg/kg | |
| 投与経路 | Orally administered | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02150733 | Completed | Hepatic Impairment|Solid Tumor|Cancer |
Daiichi Sankyo|Medpace Inc. |
April 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01892527 | Completed | Colorectal Cancer Metastatic|C-met Overexpression |
Armando Santoro MD|Istituto Clinico Humanitas |
March 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02049060 | Completed | Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma|Nonsquamous Nonsmall Cell Neoplasm of Lung |
Armando Santoro MD|Istituto Clinico Humanitas |
January 2013 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT01755767 | Completed | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
Daiichi Sankyo|ArQule Inc. a subsidiary of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC a subsidiary of Merck & Co. Inc. (Rahway NJ USA) |
December 27 2012 | Phase 3 |
|
化学情報
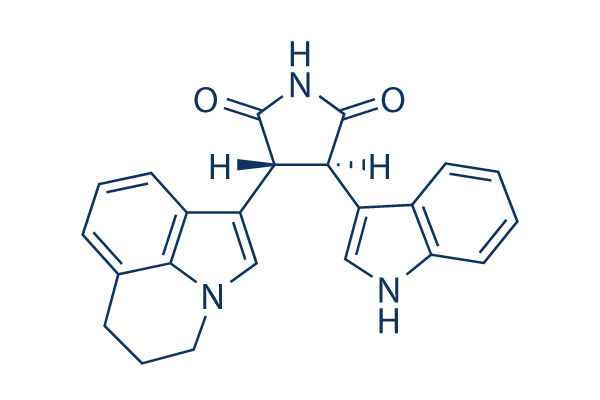
| 分子量 | 369.42 | 化学式 | C23H19N3O2 |
| CAS No. | 905854-02-6 | SDF | Download Tivantinib SDFをダウンロードする |
| Smiles | C1CC2=C3C(=CC=C2)C(=CN3C1)C4C(C(=O)NC4=O)C5=CNC6=CC=CC=C65 | ||
| 保管 | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 73 mg/mL ( (197.6 mM); 吸湿したDMSOは溶解度を減少させます。新しいDMSOをご使用ください。) Ethanol : 35 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
モル濃度計算器 |
|
in vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
投与溶液組成計算機 | |||||
実験計算
投与溶液組成計算機(クリア溶液)
ステップ1:実験データを入力してください。(実験操作によるロスを考慮し、動物数を1匹分多くして計算・調製することを推奨します)
mg/kg
g
μL
匹
ステップ2:投与溶媒の組成を入力してください。(ロット毎に適した溶解組成が異なる場合があります。詳細については弊社までお問い合わせください)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
計算結果:
投与溶媒濃度: mg/ml;
DMSOストック溶液調製方法: mg 試薬を μL DMSOに溶解する(濃度 mg/mL, 注:濃度が当該ロットのDMSO溶解度を超える場合はご連絡ください。 )
投与溶媒調製方法:Take μL DMSOストック溶液に μL PEG300,を加え、完全溶解後μL Tween 80,を加えて完全溶解させた後 μL ddH2O,を加え完全に溶解させます。
投与溶媒調製方法:μL DMSOストック溶液に μL Corn oil,を加え、完全溶解。
注意:1.ストック溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことをご確認ください;
2.順番通りに溶剤を加えてください。次のステップに進む前に溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことを確認してから加えてください。ボルテックス、ソニケーション、水浴加熱など物理的な方法で溶解を早めることは可能です。
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須
よくある質問(FAQ)
質問1:
Are there any other solutions (apart from DMSO) I can dissolve it for in vivo experiment?
回答
S2753 This compound (ARQ 197) can be dissolved in 1% methylcellulose at 15 mg/ml as a suspension.