
- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
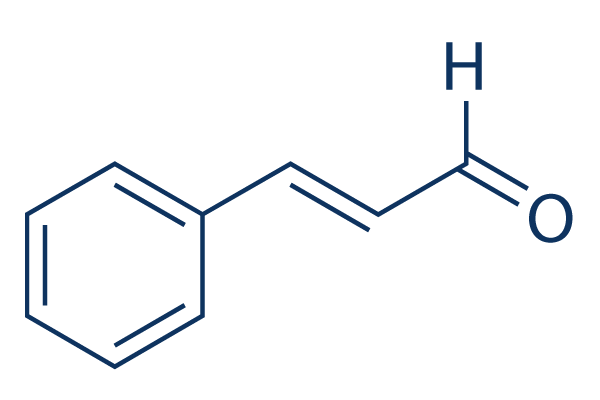
Cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamaldehydeは、シキミ酸経路によって天然に合成されるフラボノイドです。その補給は、糖尿病動物におけるグルコースおよび脂質のホメオスタシスを改善する可能性があります。TRPA1アゴニストです。
CAS No. 14371-10-9
文献中Selleckの製品使用例(3)
製品安全説明書
Cinnamaldehyde関連製品
TRP Channel阻害剤の選択性比較
生物活性
| 製品説明 | Cinnamaldehydeは、シキミ酸経路によって天然に合成されるフラボノイドです。その補給は、糖尿病動物におけるグルコースおよび脂質のホメオスタシスを改善する可能性があります。TRPA1アゴニストです。 | |
|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In Vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Cinnamaldehyde (40 μM) could enhance the expression of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), and suppress the expression of perilipin and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as well as reduce adipocyte genes expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (CEBP-α) in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. It also increases expression of PPARδ and PPARγ as well as its targeted genes such as aP2 and CD36 in 3T3-L1 differentiated adipocytes. This compound treatment increases GLUT4 expression via activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and triggering its downstream effector myocyte enhancer factors 2 (MEF2) in C2C12 cells. Its treatment regulates oxidative metabolism through increasing expressions of 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), NAD+-dependent deacetylases sirtuin 1, PGC-1α and cytochrome C as well as improving PPARα and PPARβ/δ expression, which contributes to mitochondrial biogenesis. However, it is demonstrated to inhibit mitochondrial metabolism by reducing basal and chemically-induced peak myotube oxidative metabolism in C2C12 cells. This chemical exerts cytotoxic effects on human leukemia K562 cells by inducing apoptosis and synergizing the cytotoxicity of CIK cells against K562 cells. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 細胞実験 | 細胞株 | K562 cells | ||
| 濃度 | 120 or 180 μmol/L | |||
| 反応時間 | 4, 9, or 24 h | |||
| 実験の流れ | K562 cells are treated with various concentrations of this compound for 4, 9, or 24 h. Cells are harvested and labeled with Annexin V conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (Annexin V-FITC) and PI. The cells are then analyzed by flow cytometry. Apoptotic cells are defined as Annexin V-positive and PI-negative cells (early apoptotic cells) plus Annexin V-positive and PI-positive cells (late apoptotic cells). | |||
| In Vivo | ||
| In Vivo | Cinnamaldehyde exhibits glucolipid lowering effects in diabetic animals by increasing glucose uptake and improving insulin sensitivity in adipose and skeletal muscle tissues, improving glycogen synthesis in liver, restoring pancreatic islets dysfunction, slowing gastric emptying rates, and improving diabetic renal and brain disorders. This compound exerts these effects through its action on multiple signaling pathways, including PPARs, AMPK, PI3K/IRS-1, RBP4-GLUT4, and ERK/JNK/p38MAPK, TRPA1-ghrelin and Nrf2 pathways. In addition, this compound seems to regulate the activities of PTP1B and α-amylase. Oral administration of this chemical ranging from 20mg/kg to 40 mg/kg per day for a duration lasting from 21 to 60 days results in a significant improvement in the levels of blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) as well as insulin sensitivity in STZ-induced diabetic rats. It is not stable in the body, with the possibility of metabolizing into cinnamic acid and transforming into cinnamyl alcohol. Excessive doses of this compound may generate the toxic response. In human, 3% of this substance may cause skin irritation. It is demonstrated to decrease serum IL-1β and inhibit inflammatory gene expression (COX-2, MCP-1, TNF-α, and IL-6) in WAT of HFD insulted male Swiss albino mice and C57BLKS db/db mice, while increased expression of Cpt1a protects against pro-inflammatory adipokines release and promotes fatty acid oxidation, which contributes to an improvement in insulin resistance. | |
|---|---|---|
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05654298 | Completed | Migraine |
Universitaire Ziekenhuizen KU Leuven |
March 15 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT04183283 | Completed | Healthy |
Eli Lilly and Company |
December 12 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04415892 | Unknown status | Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy |
Universitaire Ziekenhuizen KU Leuven |
October 1 2019 | Not Applicable |
|
化学情報
| 分子量 | 132.16 | 化学式 | C9H8O |
| CAS No. | 14371-10-9 | SDF | Download Cinnamaldehyde SDFをダウンロードする |
| 密度 | 1.05 g/mL at 25 °C | ||
| 保管 | 2 years -20°C liquid | ||
|
In vitro |
|
モル濃度計算器 |
|
in vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
投与溶液組成計算機 | |||||
実験計算
投与溶液組成計算機(クリア溶液)
ステップ1:実験データを入力してください。(実験操作によるロスを考慮し、動物数を1匹分多くして計算・調製することを推奨します)
mg/kg
g
μL
匹
ステップ2:投与溶媒の組成を入力してください。(ロット毎に適した溶解組成が異なる場合があります。詳細については弊社までお問い合わせください)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
計算結果:
投与溶媒濃度: mg/ml;
DMSOストック溶液調製方法: mg 試薬を μL DMSOに溶解する(濃度 mg/mL, 注:濃度が当該ロットのDMSO溶解度を超える場合はご連絡ください。 )
投与溶媒調製方法:Take μL DMSOストック溶液に μL PEG300,を加え、完全溶解後μL Tween 80,を加えて完全溶解させた後 μL ddH2O,を加え完全に溶解させます。
投与溶媒調製方法:μL DMSOストック溶液に μL Corn oil,を加え、完全溶解。
注意:1.ストック溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことをご確認ください;
2.順番通りに溶剤を加えてください。次のステップに進む前に溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことを確認してから加えてください。ボルテックス、ソニケーション、水浴加熱など物理的な方法で溶解を早めることは可能です。
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須
