- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
AG-490
別名:Tyrphostin B42, Zinc02557947
AG-490は、無細胞アッセイにおいてIC50が0.1 μMのEGFR阻害剤であり、ErbB2と比較してEGFRに対して135倍選択性が高く、Lck、Lyn、Btk、Syk、Srcには活性を示さずJAK2も阻害します。
CAS No. 133550-30-8
文献中Selleckの製品使用例(133)
製品安全説明書
現在のバッチを見る:
純度:
99.99%
99.99
AG-490関連製品
シグナル伝達経路
EGFR阻害剤の選択性比較
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | 活性情報 | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPT1 | Apoptosis Assay | 50 μM | 24/48 h | enhances TRAIL-induces cell apoptosis | |
| Jurkat | Apoptosis Assay | 50 μM | 24/48 h | enhances TRAIL-induces cell apoptosis | |
| SUPT1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | enhances TRAIL-induces cell growth inhibition | |
| Jurkat | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | enhances TRAIL-induces cell growth inhibition | |
| PA-1 | Function Assay | 10 uM | 1 h | inhibits LPA-induced ovarian cancer cell motility | |
| OVCAR-3 | Function Assay | 10 uM | 1 h | inhibits LPA-induced ovarian cancer cell motility | |
| PA-1 | Function Assay | 10 uM | 1 h | inhibits LPA-induced STAT3 phosphorylation | |
| OVCAR-3 | Function Assay | 10 uM | 1 h | inhibits LPA-induced STAT3 phosphorylation | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 15 μm | 1 h | inhibits the phosphorylation of STAT1 on tyrosine 701 was detected 15 min after SPE B treatment | |
| BMMC | Function Assay | 0-10 μM | 15 min | inhibits LTC4 release in a dose-dependent fashion with near complete inhibition at concentrations ⩾10 μM | |
| THP1 | Function Assay | 10 uM | 30 min | inhibits STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation by over 60% | |
| SW1990 | Invasion Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | reduces invasion of SW1990 cells | |
| SW1990 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | decreases the intensity of p-Stat3 expression | |
| SW1990 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | decreases the expression of MMP-2 and VEGF mRNAs | |
| SW1990 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 20 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth time dependently | |
| MZ-304 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces transcription of MMP genes and reduces enzymatic activity of MMPs | |
| MZ-256 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces transcription of MMP genes and reduces enzymatic activity of MMPs | |
| MZ-54 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces transcription of MMP genes and reduces enzymatic activity of MMPs | |
| MZ-18 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces transcription of MMP genes and reduces enzymatic activity of MMPs | |
| A-172 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces transcription of MMP genes and reduces enzymatic activity of MMPs | |
| MZ-304 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | inhibits invasion | |
| MZ-256 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | inhibits invasion | |
| MZ-54 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | inhibits invasion | |
| MZ-18 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | inhibits invasion | |
| A-172 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | inhibits invasion | |
| MZ-304 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | inhibits migration | |
| MZ-256 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | inhibits migration | |
| MZ-54 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | inhibits migration | |
| MZ-18 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | inhibits migration | |
| A-172 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | inhibits migration | |
| MZ-304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | leads to a statistically significant reduction of cell proliferation over a time period of 48 h | |
| MZ-256 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | leads to a statistically significant reduction of cell proliferation over a time period of 48 h | |
| MZ-54 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | leads to a statistically significant reduction of cell proliferation over a time period of 48 h | |
| MZ-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | leads to a statistically significant reduction of cell proliferation over a time period of 48 h | |
| A-172 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | leads to a statistically significant reduction of cell proliferation over a time period of 48 h | |
| MZ-304 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces the levels of constitutively activated STAT3 in a time-dependent and dose-dependent fashion | |
| MZ-256 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces the levels of constitutively activated STAT3 in a time-dependent and dose-dependent fashion | |
| MZ-54 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces the levels of constitutively activated STAT3 in a time-dependent and dose-dependent fashion | |
| MZ-18 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces the levels of constitutively activated STAT3 in a time-dependent and dose-dependent fashion | |
| A-172 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | reduces the levels of constitutively activated STAT3 in a time-dependent and dose-dependent fashion | |
| HEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100 μM | 0-5 d | reduces growth of JAK2V617F-expressing HEL cells | |
| HEL | Function Assay | 100 μM | 12-72 h | inhibits the level of p-JAK2, JAK2 | |
| KF8 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1 h | inhibits IL-33-induced IκBα degradation and NF-κB activation | |
| KF8 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1 h | inhibits IL-33-induced NF-κB activation | |
| Hep-2 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | downregulates the STAT3, p-STAT3 and survivin protein levels | |
| Hep-2 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits G1 to S cell cycle transition and induces G1 cell cycle arrest | |
| Hep-2 | Apoptosis Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | induces cell apoptosis time dependently | |
| Hep-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 25-100 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | |
| HSC-T6 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 2 h | inhibits the expressions of pY-STAT1 and Bad induced by CDE | |
| HSC-T6 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 2 h | inhibits the apoptosis of HSC-T6 cells induced by CDE | |
| ARPE-19 | Function Assay | 5 μM | 30 min | inhibits JAK2 phosphorilation | |
| HT29 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24/48/72 h | decreases the pSTAT3 levels in a time-dependent manner | |
| SW1116 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24/48/72 h | decreases the pSTAT3 levels in a time-dependent manner | |
| HT29 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24/48/72 h | decreases the expression of JAK2 and pJAK2 time-dependently | |
| SW1116 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24/48/72 h | decreases the expression of JAK2 and pJAK2 time-dependently | |
| RPE | Function Assay | 30 µM | 3 h | inhibits the induction of p-STAT3 expression | |
| SW620 | Function Assay | 20 µM | 1/6 h | inhibits p-STAT3 activation | |
| NRK-52E | Function Assay | 5 μM | 30 min | attenuates Ang-(1–7)-inhibited TGF-β1 mRNA at 16 h | |
| BV-2 | Function Assay | 20 µM | 16 h | inhibits LPS-induced STAT1 phosphorylation with almost completely diminished iNOS expression | |
| HUVECs | Apoptosis Assay | 20 µM | 4 h | significantly decreases the cell apoptotic index | |
| HUVECs | Cell Viability Assay | 20 µM | 4 h | attenuates H2O2-induced cell shrinkage and improved the attachment rate of the cells | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 10/20/40 μM | 24 h | suppresses the radiation-induced elevation of VEGF | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 20/40 μM | 20 h | 20 μM AG490 suppresses the radiation-induced invasion of A549 cells | |
| RAW264.7 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48 h | inhibits RANKL-induced NFATc1 expression and phosphorylation of Ser727STAT3 | |
| RAW264.7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-50 μM | 48 h | causes an arrest of RAW264.7 cells at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle | |
| RAW264.7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-50 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth dose-dependently | |
| RAW264.7 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48 h | suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 12/24 h | inhibits STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation | |
| 7TD1-WD-90 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 6 h | significantly inhibits the phosphorylation of JAK2 and phosphorylation of STAT3 | |
| 7TD1-WD-90 | Apoptosis Assay | 50 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | |
| 7TD1-DXM | Apoptosis Assay | 50 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | |
| 7TD1-WD-90 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth | |
| 7TD1-DXM | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 4 h | inhibits HSE-induced BMP7 and GHR protein expression | |
| AGS | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | the cytoplasmic localization of pJAK2 (JAK2 phosphorylated at residues Tyr1007 and Tyr1008) decreased after AG490 treatment for 24 and 48 hr, but started to rebound at 72 hr | |
| SGC7901 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | the cytoplasmic localization of pJAK2 (JAK2 phosphorylated at residues Tyr1007 and Tyr1008) decreased after AG490 treatment for 24 and 48 hr, but started to rebound at 72 hr | |
| AGS | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | the levels of pJAK2 began to decline at 24 hr, and rebounded at 72 hr | |
| SGC7901 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24/48/72 h | the levels of pJAK2 began to decline at 24 hr, and rebounded at 72 hr | |
| AGS | Cell Viability Assay | 0-100 μM | 24/48/72 h | causes a significant reduction in cell viability dose-dependently but not time-dependently | |
| SGC7901 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-100 μM | 24/48/72 h | causes a significant reduction in cell viability dose-dependently but not time-dependently | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 50-500 μM | 60 min | inhibits the IL-6-induced phosphorylation of STAT1 (Tyr705) and STAT3 (Tyr705) in a dose-dependent manner | |
| EJ | Function Assay | 50/80 μM | 48 h | downregulates c-Myc, cyclinD1, survivin and VEGF expressions | |
| EJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/80 μM | 48 h | causes S-phase arrest | |
| EJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50/80 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | |
| HSC | Function Assay | 20 μM | 1 h | abrogates the differential effects of leptin or AGEs | |
| NRK-52E | Function Assay | 1 µM | 10 min | blocks Ang II induced CD24 expression | |
| NRK-52E | Function Assay | 1 µM | 10 min | blocks the stimulatory effect of Ang II on Pax-2 expression | |
| GL37 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-10 µM | 48 h | suppresses La expression | |
| TRPM2/HEK | Function Assay | 10 µM | 40 min | reduces TRPM2 activation even at high concentrations of H2O2 | |
| U937 | Function Assay | 0.1–25 µM | 15 min | reduces H2O2-induced Ca2+increase in a concentration-dependent manner, and the IC50 value was 0.4 µM | |
| TRPM2/HEK | Function Assay | 0.1–25 µM | 15 min | reduces H2O2-induced Ca2+increase in a concentration-dependent manner, and the IC50 value was 1.7 µM | |
| B16-F0 | Function Assay | 50/100 µM | 48 h | reduces anoikis resistance | |
| SK-MEL-2 | Function Assay | 50/100 µM | 48 h | reduces anoikis resistance | |
| SK-MEL-5 | Function Assay | 50/100 µM | 48 h | reduces anoikis resistance | |
| MeWo | Function Assay | 50/100 µM | 48 h | reduces anoikis resistance | |
| SK-MEL-28 | Function Assay | 50/100 µM | 48 h | reduces anoikis resistance | |
| BCBL1 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24 h | induces a complete autophagic flux | |
| BC3 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24 h | induces a complete autophagic flux | |
| BCBL1 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24 h | mediates de-phosphorylation of STAT3 correlated with HSP70 and HSF2 reduction | |
| BC3 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24 h | mediates de-phosphorylation of STAT3 correlated with HSP70 and HSF1 reduction | |
| BCBL1 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24 h | mediates PEL cell apoptosis | |
| BC3 | Function Assay | 100 µM | 24 h | mediates PEL cell apoptosis | |
| 他の多くの細胞株試験データをご覧になる場合はこちらをクリックして下さい | |||||
生物活性
| 製品説明 | AG-490は、無細胞アッセイにおいてIC50が0.1 μMのEGFR阻害剤であり、ErbB2と比較してEGFRに対して135倍選択性が高く、Lck、Lyn、Btk、Syk、Srcには活性を示さずJAK2も阻害します。 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In Vitro | ||||
| In vitro |
AG-490 inhibits HER-2 driven cell proliferation with IC50 of 3.5 μM. Corresponding to the specific dose-dependent inhibition of constitutively activated JAK2 in pre-B acute leukemia (ALL) cells, this compound (5 μM) almost completely blocks the growth of all ALL cells by inducing programmed cell death, with no deleterious effect on normal hematopoiesis. This chemical does not inhibit the activities of Lck, Lyn, Btk, Syk, and Src. It (60-100 μM) blocks the constitutive activation of Stat3sm, and inhibits spontaneous as well as interleukin 2-induced growth of mycosis fungoides (MF) tumor cells with IC50 values of 75 μM and 20 μM, respectively. This compound potently inhibits IL-2-mediated human T cell growth with an IC50 of 25 μM by blocking the activities of JAK3 and STAT5a/b. It significantly inhibits the constitutive activation of Stat3 in MOPC, MPC11, and S194 cells, leading to dramatic dose-dependent apoptosis. This chemical (100 μM) inhibits Akt phosphorylation, inhibits the activation of nuclear factor-κB, and causes the activation of GSK-3β, leading to the reduction of c-Myc. It (50 μM) can induce apoptosis of BaF3 cells expressing T315I and E255K mutants of Bcr-Abl. This compound at 30 μM inhibits not only Epo-induced phosphorylation of wild-type JAK2 but also constitutive phosphorylation of the JAK2 V617F mutant. It also potently inhibits cytokine-independent cell growth induced by the JAK2 V617F mutant in BaF3 cells. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Assay | In vitro kinase autophosphorylation | |||
| AG-490 is dissolved in DMSO 10%-H2O-ethanol 45%. Crude membrane extracts (0.125 μg/mL) are preactivated with EGF (20 nM) in 50 mM HEPES buffer, pH 7.6, and 125 mM NaCl, for 15 minutes at 4 °C. Autophosphorylation activity of EGFR or ErbB2 kinase is assayed at 4 °C for 30 seconds in V-shaped 96-well plates. Membrane extracts (8 μL) are added to each well containing reaction mixture (12 μL, 50mM, HEPES, pH 7.4,125 mM NaCl, 12 mM M8Ac2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM NaVO3, 1 μM ATP, and 1 μCi[γ-32P]ATP, final concentrations) and increasing concentrations of this compound (4 μL). After termination by addition of hot sample buffer, the samples are run on a 6% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis minigel, the gels dried, and autoradiography performed during the linear exposure time period. The receptor bands are scanned densitrometrically, and the results analyzed by the Ez-Fit program. For the analysis of autophosphorylation of JAK2, JAK2 is immunoprecipitated by using anti-JAK2 antibody from lysates of G2 cells pretreated for 16 hours with increasing concentrations of this chemical (0-50 μM). Immune complexes are then immunoblotted with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. A dose-dependent inhibition of in vitro kinase activity is demonstrated by assessing JAK2 autophosphorylation. | ||||
| 細胞実験 | 細胞株 | Pre-B ALL | ||
| 濃度 | Dissolved in DMSO, final concentrations ~ 50 μM | |||
| 反応時間 | 16 hours | |||
| 実験の流れ | Cells are exposed to different concentrations of AG-490 for 16 hours. For the determination of cell proliferation, [3H]tymidine (1 μCi) is added 6 hours or more before the cultures are terminated. Cells are then collected and samples counted in a liquid scintillation counter. | |||
| In Vivo | ||
| In Vivo |
Administration of AG-490 drastically reduces the numbers of CD45+ and HLA-DR+ cells from 48 % and 46% in bone marrow of untreated mice, as well as 38% and 22% in the spleen of untreated mice to undetectale levels. In vivo administration of this compound causes murine myeloma tumor cell apoptosis but does not inhibit IL-12-mediated macrophage activation and IFN-γ production by lymphocytes. Consistent with the in vitro blocking of JAK2 V617F mutant activity, treatment with this chemical at 0.5 mg/day for 10 days effectively inhibits JAK2 V617F mutant-induced tumorigenesis and tumor cell invasion in nude mice. Combined therapy with this agent and IL-12 induces greater antitumor effects than either agent alone in a murine myeloma tumor model. |
|
|---|---|---|
| 動物実験 | 動物モデル | SCID mice intravenously injected with ALL cells |
| 投与量 | 0.85 mg + 0.5 mg daily | |
| 投与経路 | Continuous pump infusion supplemented with daily intraperitoneal injections | |
|
化学情報
| 分子量 | 294.30 | 化学式 | C17H14N2O3 |
| CAS No. | 133550-30-8 | SDF | Download AG-490 SDFをダウンロードする |
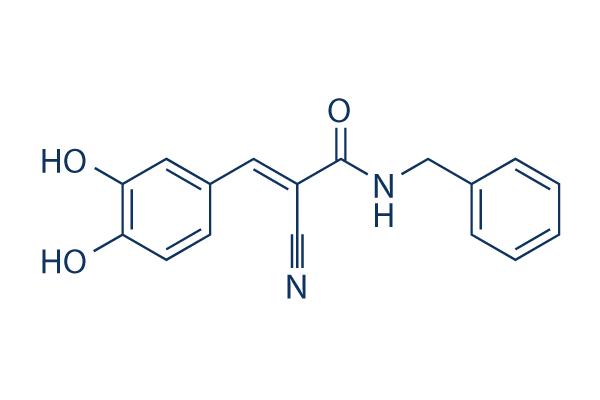
| Smiles | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CNC(=O)C(=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)C#N | ||
| 保管 | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 59 mg/mL ( (200.47 mM); 吸湿したDMSOは溶解度を減少させます。新しいDMSOをご使用ください。) Ethanol : 6 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
モル濃度計算器 |
|
in vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
投与溶液組成計算機 | |||||
実験計算
投与溶液組成計算機(クリア溶液)
ステップ1:実験データを入力してください。(実験操作によるロスを考慮し、動物数を1匹分多くして計算・調製することを推奨します)
mg/kg
g
μL
匹
ステップ2:投与溶媒の組成を入力してください。(ロット毎に適した溶解組成が異なる場合があります。詳細については弊社までお問い合わせください)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
計算結果:
投与溶媒濃度: mg/ml;
DMSOストック溶液調製方法: mg 試薬を μL DMSOに溶解する(濃度 mg/mL, 注:濃度が当該ロットのDMSO溶解度を超える場合はご連絡ください。 )
投与溶媒調製方法:Take μL DMSOストック溶液に μL PEG300,を加え、完全溶解後μL Tween 80,を加えて完全溶解させた後 μL ddH2O,を加え完全に溶解させます。
投与溶媒調製方法:μL DMSOストック溶液に μL Corn oil,を加え、完全溶解。
注意:1.ストック溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことをご確認ください;
2.順番通りに溶剤を加えてください。次のステップに進む前に溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことを確認してから加えてください。ボルテックス、ソニケーション、水浴加熱など物理的な方法で溶解を早めることは可能です。
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須
よくある質問(FAQ)
質問1:
I would like to know whether it (S1143) goes to CNS through BBB, or not?
回答
It can go through the BBB, as shown in this reference: http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/content/111/4/2062.full.html.